💻 Python Colab Gemini
การโปรแกรมและประยุกต์ใช้งาน Python Colab
ใช้ Gmail ในการสมัคร มีตัวอย่างและคำอธิบายดังด้านล่าง
- Google Colab: https://colab.research.google.com
- ระบบ Gemini: https://deepmind.google/technologies/gemini/
- YouTube Channel: @iTForLifebyAjNu
วิดีโอสอน Python Colab
EP1 ติดตั้งและใช้งาน Google Colab | เริ่มต้นใช้งาน Google Colab
EP2 Python Variable & Operator | ตัวแปร และเครื่องหมายทางคณิตศาสตร์
EP6 ตัวดำเนินการเปรียบเทียบในภาษา Python | Comparison Operator
Colab Features | ตารางแบบอินเทอร์แอกทีฟ มุมมองประวัติโค้ด
ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับ Colab | Introduction to Colaboratory
ระบบ Gemini คืออะไร?
ระบบ Gemini หมายถึงระบบปัญญาประดิษฐ์ (AI) ประเภทโมเดลภาษาขนาดใหญ่ (LLM) ที่ Google พัฒนาขึ้น
จุดเด่นของ Gemini:
- ความสามารถหลากหลาย: แปลภาษา เขียนข้อความสร้างสรรค์ ตอบคำถาม วิเคราะห์ข้อมูล เขียนโค้ด
- ความแม่นยำสูง: ผลลัพธ์ใกล้เคียงกับงานที่มนุษย์ทำ
- ใช้งานง่าย: ผู้ใช้ทั่วไปสามารถใช้งานได้โดยไม่ต้องมีความรู้ทางเทคนิค
- มีประสิทธิภาพ: ทำงานได้รวดเร็ว
โมเดลย่อยของ Gemini:
- Gemini Ultra: โมเดลขนาดใหญ่ที่สุด เหมาะสำหรับงานที่ต้องการความละเอียดสูง
- Gemini Pro: โมเดลขนาดปานกลาง เหมาะสำหรับงานทั่วไป
- Gemini Nano: โมเดลขนาดเล็ก เหมาะสำหรับงานที่ต้องการความรวดเร็ว
Google Colab คืออะไร?
Colab หรือ “Colaboratory” ช่วยให้คุณสามารถเขียนและเรียกใช้ Python ในเบราว์เซอร์ได้ง่ายๆ
- ✅ ไม่ต้องกำหนดค่าใดๆ
- ✅ เข้าถึง GPU โดยไม่มีค่าใช้จ่าย
- ✅ แชร์ได้ง่าย
ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็น นักเรียน/นักศึกษา, นักวิทยาศาสตร์ข้อมูล, หรือ นักวิจัย AI ระบบ Colab ก็ช่วยให้งานของคุณง่ายขึ้นได้
ตัวอย่างโค้ด Python จาก Gemini
1. พิมพ์ข้อความ “Hello World!”
Python
print("Hello World!")2. แสดงผลลัพธ์ของตัวแปร
Python
x = 10
y = "Python"
print("x =", x)
print("y =", y)3. การคำนวณพื้นฐาน
Python
a = 5
b = 3
sum_result = a + b
difference = a - b
product = a * b
quotient = a / b
print("ผลรวม:", sum_result)
print("ผลต่าง:", difference)
print("ผลคูณ:", product)
print("ผลหาร:", quotient)4. การใช้เงื่อนไข if-else
Python
age = 20
if age >= 18:
print("คุณบรรลุนิติภาวะ")
else:
print("คุณยังไม่บรรลุนิติภาวะ")5. วนลูป for
Python
for i in range(5):
print(i)6. ฟังก์ชัน
Python
def say_hello():
print("Hello!")
say_hello()7. การอ่านไฟล์
Python
with open("myfile.txt", "r") as f:
content = f.read()
print(content)8. การเขียนไฟล์
Python
with open("myfile.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("This is a new file.")ตัวอย่าง Deep Learning – Image Processing
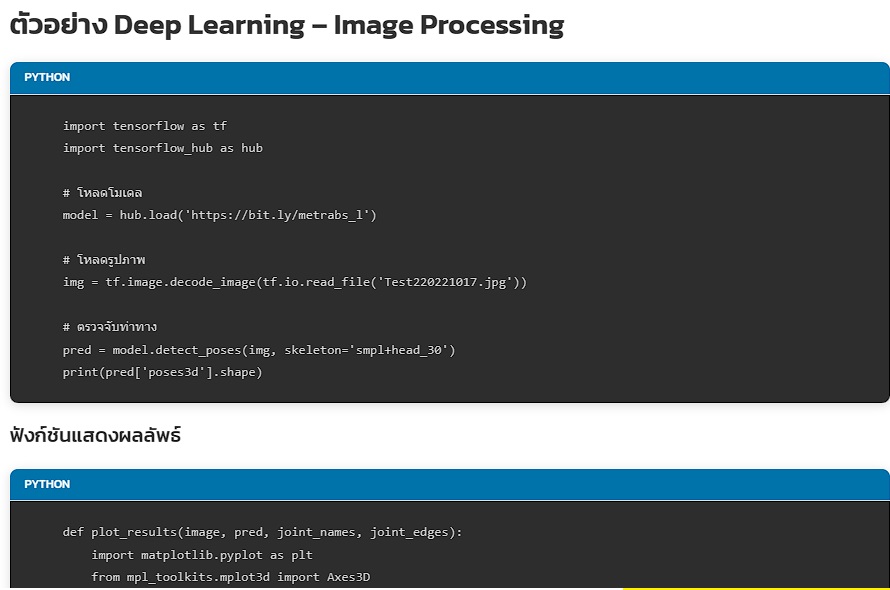
Python
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
# โหลดโมเดล
model = hub.load('https://bit.ly/metrabs_l')
# โหลดรูปภาพ
img = tf.image.decode_image(tf.io.read_file('Test220221017.jpg'))
# ตรวจจับท่าทาง
pred = model.detect_poses(img, skeleton='smpl+head_30')
print(pred['poses3d'].shape)ฟังก์ชันแสดงผลลัพธ์
Python
def plot_results(image, pred, joint_names, joint_edges):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5.2))
image_ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
image_ax.imshow(image.numpy())
for x, y, w, h, c in pred['boxes'].numpy():
image_ax.add_patch(Rectangle((x, y), w, h, fill=False))
pose_ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')
pose_ax.view_init(5, -75)
pose_ax.set_xlim3d(-1500, 1500)
pose_ax.set_zlim3d(-1500, 1500)
pose_ax.set_ylim3d(2000, 5000)
poses3d = pred['poses3d'].numpy()
poses3d[..., 1], poses3d[..., 2] = poses3d[..., 2], -poses3d[..., 1]
for pose3d, pose2d in zip(poses3d, pred['poses2d'].numpy()):
for i_start, i_end in joint_edges:
image_ax.plot(*zip(pose2d[i_start], pose2d[i_end]), marker='o', markersize=2)
pose_ax.plot(*zip(pose3d[i_start], pose3d[i_end]), marker='o', markersize=2)
image_ax.scatter(*pose2d.T, s=2)
pose_ax.scatter(*pose3d.T, s=2)
# เรียกใช้งาน
joint_names = model.per_skeleton_joint_names['smpl+head_30'].numpy().astype(str)
joint_edges = model.per_skeleton_joint_edges['smpl+head_30'].numpy()
plot_results(img, pred, joint_names, joint_edges)แหล่งข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
การทำงานกับสมุดบันทึกใน Colab
- ภาพรวมของ Colaboratory
- ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับ Markdown
- การนำเข้าไลบรารีและการติดตั้ง Dependencies
- การบันทึกและโหลดสมุดบันทึกใน GitHub
การทำงานกับข้อมูล
- การโหลดข้อมูล: ไดรฟ์ ชีต และ Google Cloud Storage
- แผนภูมิ: การแสดงข้อมูลเป็นภาพ
- การเริ่มต้นใช้งาน BigQuery
แมชชีนเลิร์นนิง
- ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับ Pandas DataFrame
- การถดถอยเชิงเส้นกับ tf.keras
- TensorFlow กับ GPU
- TensorFlow กับ TPU